Valuation of intangibles
Valuation of Intangibles
index

Importance of Valuing Intangible Assets
The appreciation and understanding of intangible resources represents one of the key aspects in the evaluation that provides a competitive advantage to ensure the sustainability and expansion of an industry or competition. Intangible assets are described as "that which lacks a physical or visible form, but can be manifested through economic interests, contracts or documents", most companies own approximately one third of their assets in the form of intangible resources, which are usually underestimated in their assessment.
What intangibles do we value?
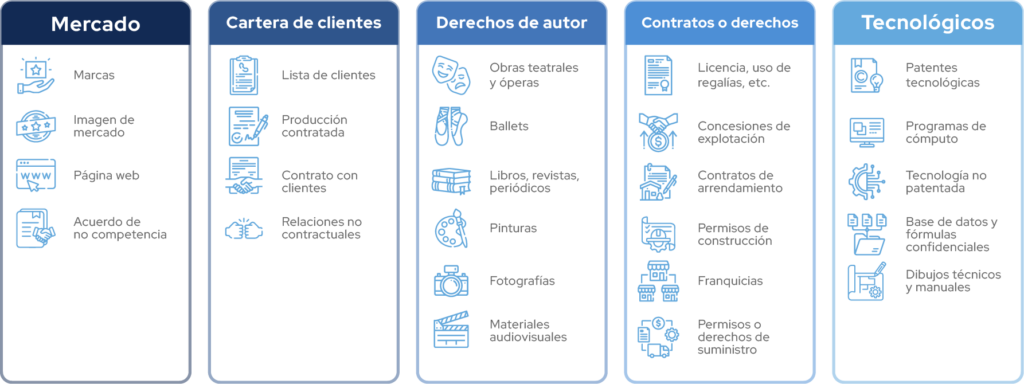
Market:
- Marks (Nominative, Unnamed, Mixed Three-Dimensional)
- Market Image
- Websites
- Non-Competition Agreement
Related to Client Portfolio:
- Client list
- Contracted Production
- Contract with Clients Non-Contractual Relationships
Intellectual or Artistic (Copyright):
- Plays, operas, ballets
- Books, magazines, newspapers,
- Paintings, Photographs, Audiovisual materials.
Contracts or Rights:
- License, use and royalties Advertising, construction, administration, service or supply contracts
- Exploitation concessions
- Lease Contracts
- Construction Permits
- Franchises
- Supply permits or rights.
Technological:
- Technological patents Research and development in process
- Computer system as well as licenses, computer programs, etc.
- Non-patented technology
- Database Processes and confidential formulas
- Technical drawings and manuals
Purpose of valuing intangibles
The objective of this valuation is mainly:
- Purchase-Sale or Transfer of Intangible
- Determine a real value of the estate
- Early Good Will Recognition
- Consolidation of Financial Reports
- Mergers
- Acquisitions
- Litigation
- Fiscal Guarantee
- Joint Venture
- Tax Strategy
Considerations for Choosing a Valuation Methodology
- Purpose and objective of the analysis
- Define the intangible asset of the subject
- Understand the legal rights subject to analysis
- Value date
- Highest and best use considerations
- Report Writing: Telling an analysis of a story must be replicable.
The following should be taken into account:
- History and development of the intangible asset
- Owner or operator, or both
- Licensee or licensor, or both
- Operations within the industry as well as price data
- Competitive environment
- Commercial corporate intangible assets, cost and treatment
Valuation methods for intangible assets
Valuation methods commonly used to assign value to intangible assets are based on the market itself and valuation requires a measure of economic value.
Income Methodology:
The revenue-based model is best used when the intangible asset generates revenue or allows the asset to generate cash flows, the earnings, like other valuation allocations, focus on future earnings from the technology transition.
Multiples Methodology:
The process is the following:
1) Quote multiples based on Net revenues – Top Line. Ex: (EV / Revenues)x
2) Quote multiples based on Operating Profits with and without D&A (EBITDA and EBIT) – Middle Line. Ex: (EV / Ebitda)x & (EV / Ebit)x
3) Price multiples based on Net Profits and Net Income per share (Bottom Line) Ex: PER (price earning ratio) Price to Sales x
Cost Methodology:
Cost-based analysis is based on alternative economic principles and generally ignores the magnitude, timing, and duration of future economic benefits, as well as the risks of operating under competitive conditions. Initial costs represent only the actual costs incurred to develop the asset. New copy price means the current price of the same property new. New replacement cost means the current cost of a similar new property. A new copy price is the current price of the same property new. New replacement value is the current price of a similar new property that has the most similar appraised value. In most cases, new replacement cost is the simplest and most meaningful cost-based approach to asset value. Different types of obsolescence, such as functional, technical, and financial, must be taken into account when estimating new replacement costs.
Other methods of valuation of intangibles
- cost method
- Market pricing method
- Income Method or (EVA)
- Valuation based on market position
- Skandia Navigator
- Relief from Royality Method
- EVE
- DCF (Dynamic Residual)
- MPEEEM
- Differential Value Methods
- WWM
- INTERBRAN Method
- VC approach
Benefits of valuing intangibles
1)Capital benefit With which the intangible business assets will be correctly valued in market parameters.
2) Financial benefit Companies with a fair valuation of intangible assets tend to be more attractive to financial institutions to provide lines of credit and financing.
ANEPSA GLOBAL
With Anepsa Global it is possible for this and other types of appraisals to be carried out, contact us by leaving your information or sending a message through our social networks, we are here to provide you with advice and guide you so that you know what type of appraisal is best for you.