Fixed Asset Consulting - Fixed Asset Management and Administration
index

Fixed asset control is essential for effective management of tangible resources in a business. These assets, which the organization acquires for the purpose of using them in the production of goods or services, are not intended for immediate sale. Fixed assets encompass a variety of assets, including property, land, buildings, machinery, equipment, and vehicles. Maintaining proper control of these assets ensures their optimal use and contributes to long-term operational efficiency.
What Fixed Assets Can Be Controlled?
Fixed assets are tangible assets acquired by an enterprise for use in its long-term operations, rather than for sale in the normal course of business. These assets provide lasting benefits to the entity and are categorized into several classes for proper management:
- Lands: They include all parcels of land owned by the company, whether urban or rural.
- Constructions in progress: Works that are in the construction phase and are not yet finished for use.
- Own buildings: Real estate properties belonging to the company, such as offices, factories, commercial premises, and other properties.
- Facilities and Improvements in Leased Properties: Modifications and improvements made to rented properties that add value to the entity.
- Machinery and Equipment: Industrial equipment, tools and machinery necessary for the daily operational functioning of the company.
- Operation Team: Specialized equipment used in daily operations, which may include specific machinery for production or processing.
- Furniture and Household Goods: Office furniture, shelves, desks, and other items used in the work environment.
- Computer Equipment: Includes computers, servers, and other technological devices used in the management and execution of operations.
- Transportation Equipment: Company-owned vehicles intended for the transport of people, goods or equipment, such as trucks, vans, and cars.
- Controllable Equipment: Devices or systems that can be monitored and managed to ensure their efficiency and functionality.
- Leased/Loaned Equipment: Goods that the company uses under a lease or loan agreement, instead of being its property.
Stages for the Management and Administration of Fixed Assets
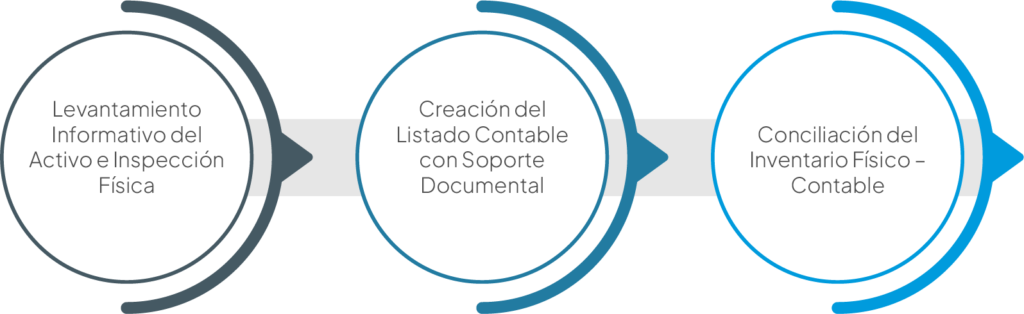
For one efficient management of fixed assets, it is essential to follow a structured process to ensure accurate and complete administration. The key steps are detailed below:
- Asset Information Survey and Physical Inspection
This stage involves collecting detailed information about each fixed asset located in the different areas of the company. A physical inspection is carried out to verify the existence, condition and location of the assets. This process ensures that all information about the assets is collected in a comprehensive and accurate manner. - Creation of the Accounting List with Documentary Support
A detailed accounting record is developed based on existing accounting information on the fixed assets. This record is enriched with relevant documentation, such as invoices, purchase orders and any other supporting documentation related to the acquisition and maintenance of the assets. The integration of these documents provides a complete and verifiable record of each asset. - Reconciliation of Physical – Accounting Inventory
At this stage, a reconciliation is performed between the accounting records of the fixed assets and the physical inventory. The information obtained during the information gathering and the creation of the accounting list is used to compare and align the accounting data with the physical assets located. An executive report is generated that summarizes the discrepancies, identifying the assets that are correctly recorded and those that do not match between the accounting records and the physical inventory. This report facilitates the identification of errors and the implementation of necessary corrections for accurate and efficient management.
Fixed Assets Advisory Solutions
With the adoption of the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)Both public and private companies are facing new challenges in fixed asset management. These challenges include meeting accounting valuation requirements and performing accurate audits of the physical inventory of assets. To effectively address these challenges, it is recommended to implement the following consulting solutions:
- Analysis and Diagnosis of the Asset Registry Conducting a thorough analysis of the asset register is essential to ensure its accuracy and completeness. This process includes a detailed review of all relevant data for each asset, such as acquisition date, cost, location, and current condition. Identifying and correcting errors in the register facilitates more accurate management and reliable valuation of assets.
- Physical Inventory and Reconciliation Performing a physical inventory is essential to verify the existence, condition, and location of assets. This involves performing visual inspections and tagging assets with barcodes, QR codes, or RFID tags to facilitate identification and tracking. The physical inventory must then be reconciled with accounting records to ensure consistency and accuracy of information.
- Multifunctional Asset Valuation Asset valuations should be conducted with multiple objectives in mind, such as financial, accounting, insurance, tax and regulatory purposes. These valuations provide an accurate estimate of the current value of assets, taking into account depreciation, wear and tear and market conditions. This multi-functional approach ensures that assets are valued appropriately in a variety of contexts.
- Asset Life Review It is crucial to periodically review the estimated useful life of assets to ensure that they operate within expected parameters. This review allows for identifying opportunities to extend the useful life through proper maintenance or, failing that, to plan the upgrade or replacement of assets at the end of their life cycle.
- Identifying Opportunities to Accelerate Depreciation A detailed analysis of assets can reveal opportunities to accelerate the depreciation of assets that are near the end of their useful life. This approach can provide tax benefits to the company through accelerated depreciation deductions, thus optimizing the tax management of assets.
- Technological Solutions with RFID RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology offers advanced solutions for automation in asset identification and tracking. These systems improve accuracy and efficiency in asset management, reducing errors and optimizing inventory and location processes.
- Fixed Asset Management Software Implementation Implementing specialized fixed asset management software is crucial for efficient management. These systems provide features such as real-time tracking, customized reports, maintenance alerts, and regulatory compliance. These tools facilitate more effective and transparent asset management, contributing to a smoother and more organized operation.
Key Steps for Fixed Asset Control in Companies
To effectively manage fixed assets, it is essential to follow a series of steps that ensure thorough and accurate control. These steps include:
- Registration and Classification Keep detailed records of all fixed assets, including key information such as date of acquisition, cost, estimated useful life and depreciation. Classify assets by nature and function to facilitate management and analysis.
- Identification and Labeling Assign each asset a unique and visible identification number, using barcode, QR or RFID tags. This makes it easier to track and locate assets, especially in multi-location environments.
- Valuation and Depreciation Calculate and record depreciation of assets over their useful lives. Depreciation reflects the loss of value due to wear and tear, obsolescence, and other factors. Use appropriate depreciation methods, such as straight-line or declining-balance, based on the needs of the business.
- Periodic Inventories Conduct physical inventories on a regular basis to verify the existence and condition of fixed assets. This process helps identify losses, thefts, or damages, and ensures that records match physical assets.
- Movement Tracking Record all asset movements, such as transfers between departments, repairs, maintenance, sales or disposals. Accurate tracking ensures effective management and prevents inconsistencies in records.
- Access Control and Security Implement security measures to protect assets from damage or theft. Restrict access to certain assets to authorized personnel only to minimize the risk of misuse or loss.
- Using Management Software Use specialized software systems for fixed asset management. These systems facilitate the monitoring, valuation and control of assets, providing detailed reports and alerts for more efficient management.
- Internal and External Audits Conduct periodic audits to verify the accuracy of records and ensure compliance with policies and procedures. Audits help identify areas for improvement and maintain the integrity of the asset management system.
How Does SAAF Help You?
He Fixed Asset Management Software (FAMS) SAAF is a comprehensive tool designed to streamline the management and tracking of fixed assets in your company. With SAAF, you can effectively manage each asset, improving accuracy and operational efficiency through a range of advanced features.
Key Benefits of SAAF:
- Quick Access to Information: Scan QR codes from any internet-connected device to quickly access any asset's record. This makes it easy to view essential information about the asset's location, status and details.
- Efficient Change Control: Monitor and manage changes to assets using configurable authorizations and permissions based on user profiles. This ensures that only authorized personnel can make changes.
- Customizable Control Panel: Adjust the control panel to your preferences to view the most relevant information in a clear and accessible way.
- Barcode and QR Code Generation: Create and assign barcodes and QR codes for accurate identification and efficient asset tracking.
- Adaptation of Formats: Customize software module formats to your company's specific needs, ensuring they fit your processes and requirements.
- Cloud Access or Web Service: Use the application through Clouding or Web Service to access the platform from anywhere and at any time.
- Attachments and Documentation: Attach photos, invoices and relevant documents to each asset, providing a complete and accessible record for each item.
- Managing Multiple Companies: Create and manage multiple companies within the platform, facilitating asset control in organizations with diversified structures.
- User and Profile Management: Control and manage user profiles, ensuring that permissions and access are appropriate for each role.
- Change History: View change history by asset to track modifications and keep a detailed record of all actions performed.
- Import and Export Data: Facilitates the import and export of fixed asset databases, allowing for seamless integration with other systems and processes.
- Generation of Safekeeping Vouchers: Issues security vouchers assigned to specific users, ensuring greater traceability and control over asset management.
Tips to Improve Fixed Asset Control in Your Company
- Assign a Fixed Asset Manager
Designating a person in charge of fixed asset control is essential for effective management. This person will be responsible for keeping information up to date, knowing the location and status of each asset, and ensuring that all data is entered correctly into the management software. In addition, it is crucial that this person receives adequate training to use the asset control software efficiently.
- Use Labels and Identification Plates
To improve asset tracking and management, make sure each asset is marked with a tag or identification plate. These tags, which can be generated directly from the software, should include key information such as the make, model, serial number, purchase date, maintenance date, and the person responsible for the asset. This makes it easier to quickly and accurately identify each asset.
- Consolidation of Information
All information related to fixed assets should be centralized in one place. Avoid dispersing information across multiple documents and use specialized software that allows for comprehensive management of all company assets. This not only improves efficiency in asset management, but also reduces the risk of errors and loss of information.
- Asset Classification
For companies with large volumes of assets, classification is essential. Organize assets into categories based on their properties, attributes, type, brand, or any other relevant characteristics. Proper classification facilitates management and inventory, allowing quick access to information and more efficient asset management.
- Constant Information Update
Keep asset information up to date on a regular basis. Constant updating ensures that data is accurate and reflects the current status of assets. This facilitates more agile and efficient control, and reduces the time required to conduct audits or asset reviews.
- Implement Asset Management Software
Using specialized fixed asset management software offers multiple benefits. These systems allow you to store all asset information, calculate depreciation, generate labels and plates, issue security vouchers, and configure maintenance alerts. In addition, many software programs allow you to manage assets from multiple companies, providing a comprehensive solution that optimizes asset control and management.



